In the digital age, online privacy and security are more important than ever. As internet users seek ways to protect their data and access restricted content, two popular solutions often come up: Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) and proxies. While both serve similar purposes, they operate differently and offer distinct advantages and disadvantages. In this article, we’ll explore the key differences between VPNs and proxies, helping you make an informed choice for your online needs.
Understanding VPNs and Proxies
What is a VPN?
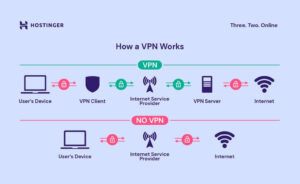
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) creates a secure, encrypted connection between your device and the internet. By routing your internet traffic through a remote server, a VPN masks your IP address and encrypts your data, providing enhanced privacy and security. VPNs are typically used for:
- Securing Public Wi-Fi Connections: Protecting your data on unsecured networks.
- Bypassing Geo-Restrictions: Accessing content available in other countries.
- Anonymity: Keeping your online activities private from ISPs and websites.
What is a Proxy?
A proxy server acts as an intermediary between your device and the internet. When you use a proxy, your requests are sent to the proxy server, which then forwards them to the target website. The website sees the proxy’s IP address instead of yours. Proxies are commonly used for:
- Accessing Restricted Content: Bypassing regional blocks on websites.
- Web Scraping: Collecting data from websites without revealing your IP.
- Caching: Storing frequently accessed data to improve loading times.
Key Differences Between VPNs and Proxies
1. Encryption
VPN: VPNs use strong encryption protocols (like AES-256) to secure your internet traffic. This means that your data is protected from eavesdroppers, making it difficult for anyone to intercept or read your information.
Proxy: Most proxies do not encrypt your data, leaving your online activities vulnerable to surveillance and interception. This lack of encryption means that while your IP address may be hidden, your data is still exposed.
2. Privacy and Anonymity
VPN: By masking your IP address and encrypting your data, VPNs offer a higher level of privacy and anonymity. They prevent ISPs and websites from tracking your online behavior, ensuring that your activities remain private.
Proxy: While proxies can hide your IP address, they do not provide the same level of privacy. Many proxies log user activities, which could potentially be accessed by third parties. This makes proxies less reliable for maintaining anonymity.
3. Speed and Performance
VPN: Because of the encryption process, VPNs can sometimes slow down your internet speed. However, reputable VPN providers offer high-speed servers that minimize latency, allowing for a smooth browsing experience.
Proxy: Proxies generally offer faster speeds since they don’t encrypt data. This makes them suitable for tasks that require quick access, such as streaming or web scraping, but at the cost of security.
4. Usage Scenarios
VPN: Ideal for users who prioritize security and privacy, such as:
- Individuals accessing sensitive information over public Wi-Fi.
- Users wanting to bypass geo-restrictions for streaming services.
- Remote workers accessing company networks securely.
Proxy: Better suited for users who need to access geo-restricted content without concern for security, such as:
- Casual internet users looking to bypass website blocks.
- Web scrapers needing to collect data from multiple sources.
5. Device Compatibility
VPN: Most VPNs offer applications for various devices, including desktops, smartphones, and routers. This allows you to protect all your internet-connected devices with a single subscription.
Proxy: Proxies can be configured on specific applications (like web browsers) but often lack support for system-wide protection. This means you may need to set up proxies for each application individually.
Which One Should You Choose?
Choosing between a VPN and a proxy depends on your specific needs:
- Choose a VPN if:
- You require strong security and privacy.
- You frequently use public Wi-Fi networks.
- You want to access geo-restricted content securely.
- Choose a Proxy if:
- You need to bypass regional restrictions quickly.
- You’re focused on speed rather than security.
- You’re using specific applications that support proxy settings.
Conclusion
Both VPNs and proxies serve valuable purposes in enhancing your online experience, but they cater to different needs. VPNs provide robust security and privacy through encryption, making them ideal for users who prioritize their data protection. Proxies, on the other hand, offer speed and simplicity for accessing restricted content but fall short in terms of security.
Call to Action
Ready to enhance your online security and privacy? Explore our top VPN Recommendations HERE today and take control of your digital presence! Whether you choose a VPN or a proxy, make sure it aligns with your online needs for a safer browsing experience.
AFFILIATE DISCLOSURE : At VPN Voyager, we believe in transparency and honesty. As a dedicated affiliate marketing site, we may earn a commission when you make a purchase through the links on our website at no extra cost to you. We only recommend products we trust and believe will benefit our readers. Your support helps us continue providing valuable content.